Describe the Structure of a Fatty Acid
The fatty acids are long chains of carbons with bonded hydrogens. Unsaturated fatty acids are liquid at room temperature.

Saturated Fatty Acid Structure Formula Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
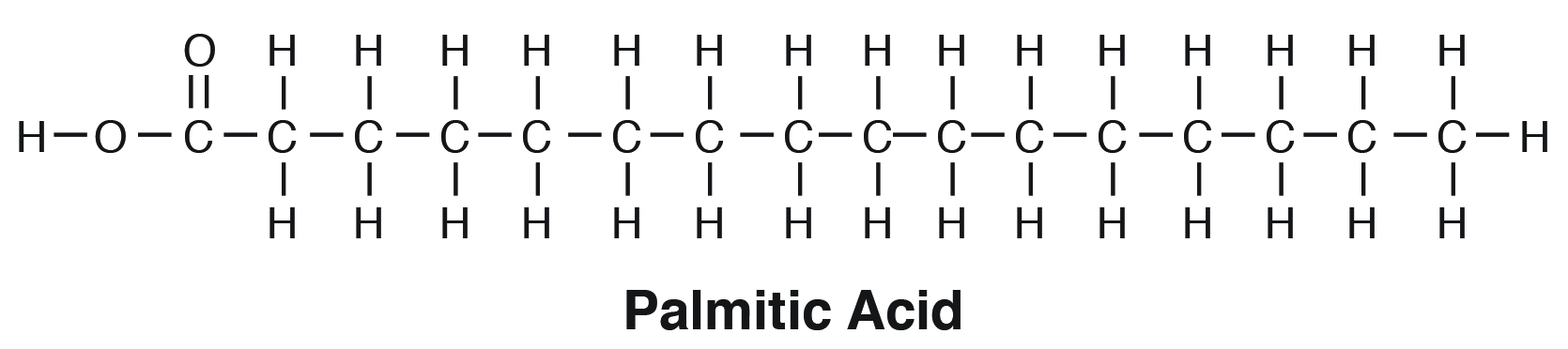
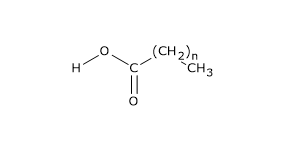
Generally a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms along the length of the chain and at one end of the chain and a carboxyl group COOH at the other end.
. The long chain length of fatty acid has a high melting point than short-chain fatty acids. At room temperature they are solid. The chain is made up of two terminals the carboxyl terminal and the hydroxyl terminal.
Most fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain and follow the general molecular formula of CH 3 CH 2 x COOH where x is the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain. Fatty acidsdiffer from one another in the number of. Describe the difference between the structure of a triglyceride molecule and the structure of a phospholipid molecule.
Fatty acids are composed largely of a chain of carbon atoms bonded with hydrogen atoms. Fatty acids are made up largely of a chain of carbon atoms bonded with hydrogen atoms. Lipids range in structure from simple short hydrocarbon chains to more complex molecules including.
Fatty Acid Definition. Saturated fatty acids SFA are fatty acids that contain no double bonds and have general formula R-COOH. It is that carboxyl group that makes it an acid carboxylic acid.
Describe the structure of fatty acids in general. A fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long side chain of hydrocarbons. These are the parts of the triglycerides that are used for energy production.
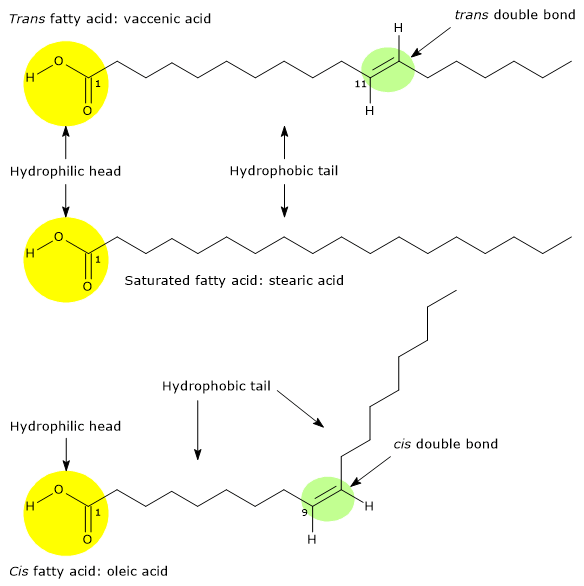
Fatty acids have methyl groups at one end of the chain and carboxyl groups on the opposite end. 175 Describe some similarities and differences in the structures of a saturated fatty acid and an unsaturated fatty acid. Fatty acids have many roles but a very common one is to form the lipids in membranes.
Fatty acids usually have an evennumber of carbon atoms because they are built from 2-carbon molecules. Regulation of intracellular signaling pathways. All fatty acids have a long chain and carboxylic acid on end.
Only a single bond hydrocarbon chain with no double bond. What is similar between the structure of phosphoglycerides and sphingolipids. They are unsaturated with hydrogen but can be hydrogenated chemically.
The solubility of fatty acids decrease due to increase in no. The most common type of lipids is called triglycerides. So stearic acid has 18 carbon atoms and is related to the alkane with 18 carbon atoms ie.
At one of the terminal ends of a fatty acid is a carboxyl group -COOH. A saturated fatty acid contains only single bonds while an unsaturated fatty acid contains double bonds. The melting point of.
Fatty acids vary in length and the presence of double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain. The carboxyl terminal consist of a carboxyl group which is the reactive portion of the molecule which participate in chemical reactions while the hdyroxy terminal of the chain consists of the. To obtain the.
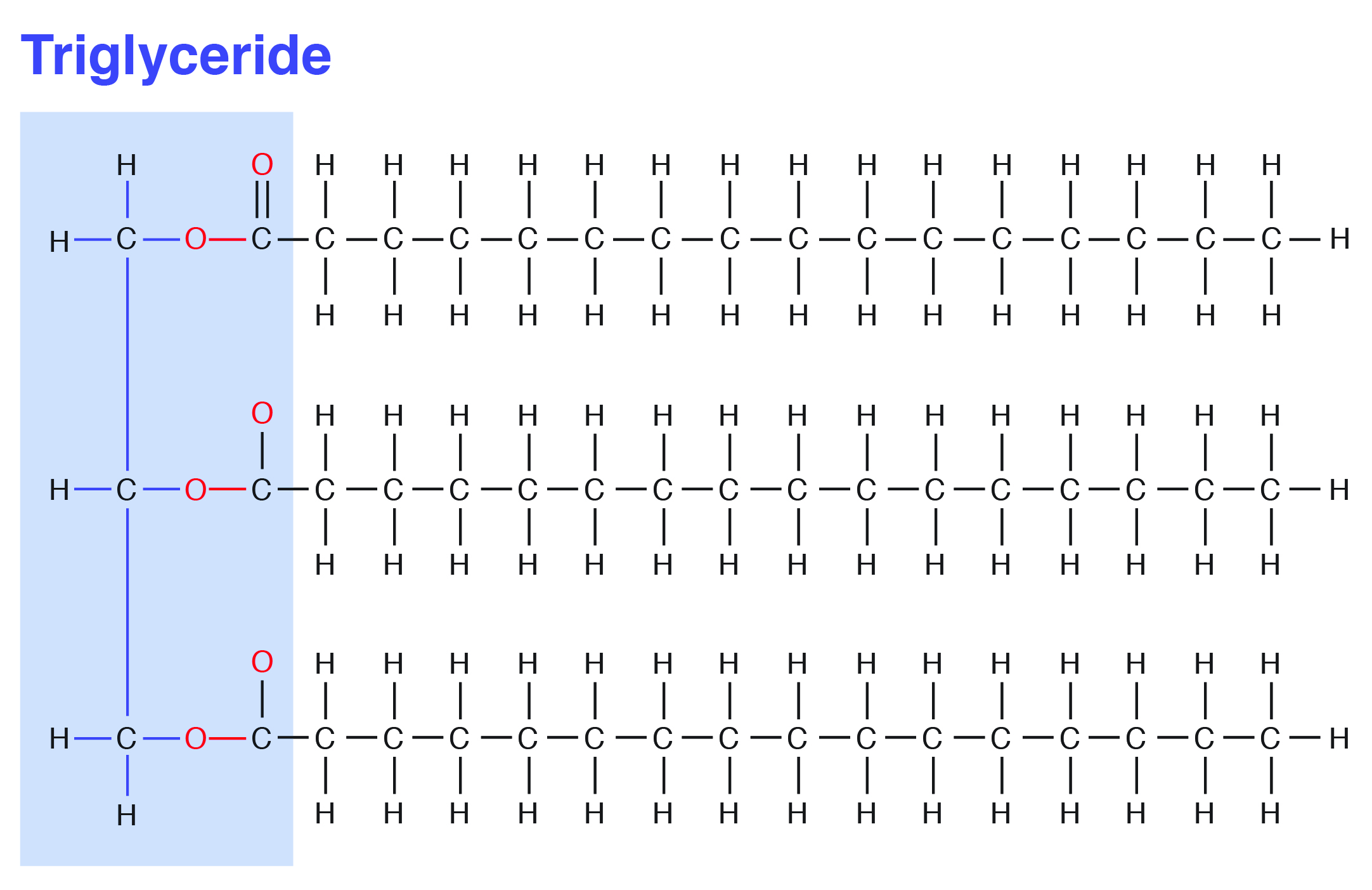
The fatty acids in the triglyceride could be the same or could have different structures. Fatty acids are chains of carbon atoms between 14 and 22 with the end carbon possessing a carboxyl group COOH. Glycerol is a trihydric alcohol.
The carbon connected to the carboxyl group is called the alpha carbon and the methyl group carbon is known as the omega carbon. Ignore references to saturated and unsaturated Accept Reject PPhosphorus Accept annotated diagrams. Its general formula is CnH2nO2 where there are twice as many hydrogen atoms as there are carbon atoms and there are always two oxygen atoms.
Fatty acid is a carboxylic acid consisting of a hydrocarbon chain and a terminal carboxyl group especially any of those occurring as esters in fats and oils. _____________ _____________ are carboxylic acids that typically contain between 12 and 20 carbon atoms. In turn the name of the fatty acids refers back to the name of the saturated hydrocarbon with the same number of carbon atoms.
One or more double bonds hydrocarbon chain. Triglycerides are made up of 3 fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol backbone. Fatty acids are energy sources and membrane constituents.
At room temperature they are liquid. They have biological activities that act to influence cell and tissue metabolism function and responsiveness to hormonal and other signals. Fatty acids are fats that have acidic carboxyl groups on them.
The biological activities may be grouped as regulation of membrane structure and function. 121 Saturated acids Fatty acids are named according to the number of carbon atoms in the chain. In phospholipid one fatty acid replaced by a phosphate.
Saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature. Why are phospholipids amphipathic. Physical Properties of Fatty Acid.
The fatty acids can be different types and the fatty acid structure defines the type of triglyceride. Why is olive oil liquid at room temperature and margarine solid. Many food sources have saturated fatty acids present.
Describe the structure and function of fatty acid molecules. The purpose of this article is to describe the structure function and metabolism of fatty acids and lipids that are of particular importance in the context of parenteral nutrition. Something like CH3-CH2n-COOH Unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds between 1 or more of the carbons in the chain.
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Lipids 2. Which cell organelles have a double membrane. Olive oil and margarine are both lipid-based food products.
Lipids are a heterogeneous group of molecules that share the common property of hydrophobicity. Basic Structure of Fatty Acids. The R- group is a straight-chain hydrocarbon of the form CH 3 CH 2 n with varying length ranging from short chain length volatile liquids to chain lengths of 30 or more carbon atoms waxy solids though the most common and important fatty acids found in many.
Vi Lipids Structure A Guide To The Principles Of Animal Nutrition

Saturated Fatty Acid Structure Formula Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Trans Fatty Acids Definition Structure Health Effects Sources

Fatty Acid Definition Structure Functions Properties Examples Britannica

Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fatty Acids Classification Of Fatty Acids

Structures Of Omega 6 And Omega 3 Fatty Acids Omega 3 Fatty Acids Download Scientific Diagram

Triacylglycerol Tag Structure Showing Glycerol With Three Fatty Acids Download Scientific Diagram
Vi Lipids Structure A Guide To The Principles Of Animal Nutrition

Fatty Acids Definition Structure Function Types Biology Dictionary

Fatty Acids Definition Structure And Classification
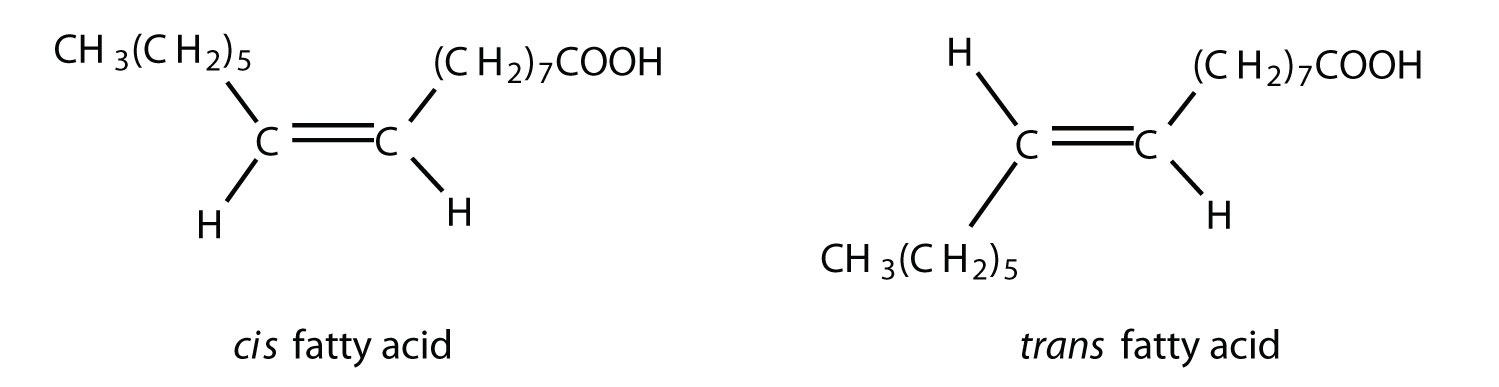
17 1 Fatty Acids Chemistry Libretexts

Omega 3 Fatty Acid Structure Types Sources And Benefits

Structure And Nomenclature Of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Pufas Cx Y Download Scientific Diagram

Fatty Acids Cell Signaling Learn Science At Scitable

Fatty Acids Definition Structure Function Types Biology Dictionary
Saturated Fatty Acids Definition Structure Examples Tuscany Diet

